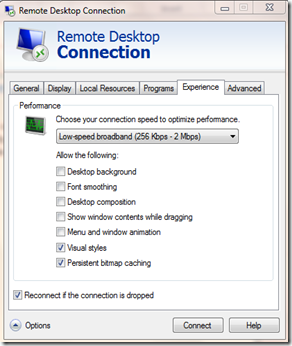
Remote Desktop has allowed network administrators to remotely manage servers for years. While studying Remote Desktop settings this past week, we were looking at the possible experience settings below.
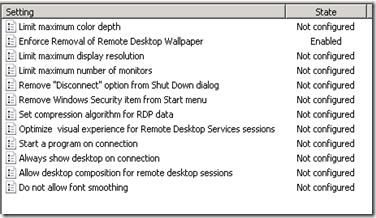
From these settings, you can control how much visual data is set from the target server to your remote session on your computer. The question was is there a way to set the experience level on the target server and override what the user wants? Using group policy, you can. Take a look at the settings below that can be found at Computer Configuration \ Policies \ Administrative Templates \ Windows Components \ Remote Desktop Services \ Remote Desktop Session Host \ Remote Session Environment
To demo the target override, I set the GPO to Enforce Removal of Remote Desktop Wallpaper. Here is a very annoying desktop background that I put on my server while logged in locally.
Below is the same view while logged in using RDP.
My RDP settings were set to Allow Desktop, but the GPO enforced on the target was set to Enforce Removal of Remote Desktop Wallpaper.


Comments